Republic Day, or Gantantra Divas, celebrated annually on January 26th, holds great significance in the hearts of every Indian. This day marks the adoption of the Constitution of India, turning the nation into a sovereign, socialist, secular, and democratic republic. As we commemorate the 75th Republic Day, let us learn some amazing facts about Indian Constitution.
This is a very good opportunity for students to dive into the history of this herculean task that the makers of constitutions took after India became independent in 1947.
1. The Longest Constitution in the World:

The Indian Constitution holds the distinction of being the longest constitution globally. Enacted on January 26, 1950, it is a comprehensive document that outlines the fundamental principles, rights, and duties of citizens, as well as the structure and functioning of the government. To this date, the Constitution has 448 articles in 25 parts and 12 schedules. There are 104 amendments that have been made to the Indian Constitution so far.
2. A Handwritten Constitution:
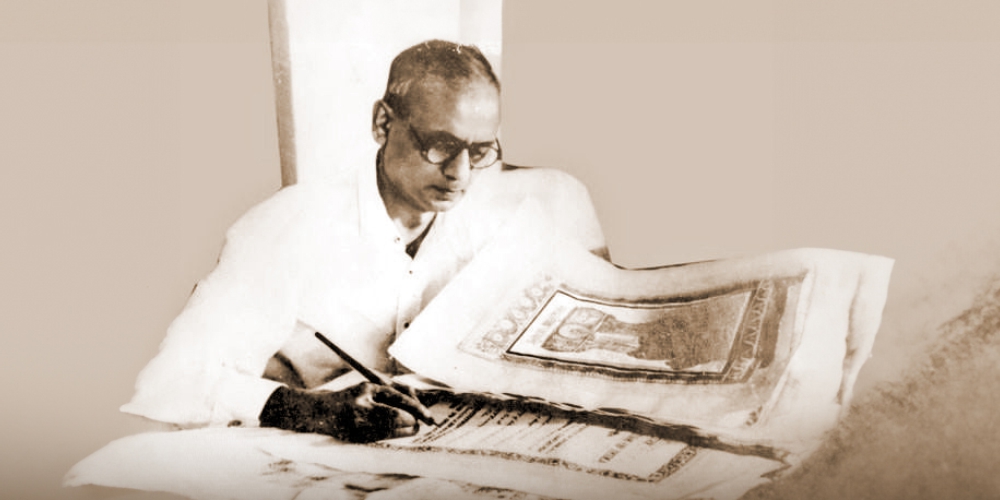

The process of drafting the Indian Constitution was an elaborate and meticulous one. The Indian Constitution is not produced through traditional writing or printing methods. Instead, both the Hindi and English versions are meticulously handwritten in a flowing italic style by Prem Behari Narain Raizada.
3. Preservation of the Original Constitution:
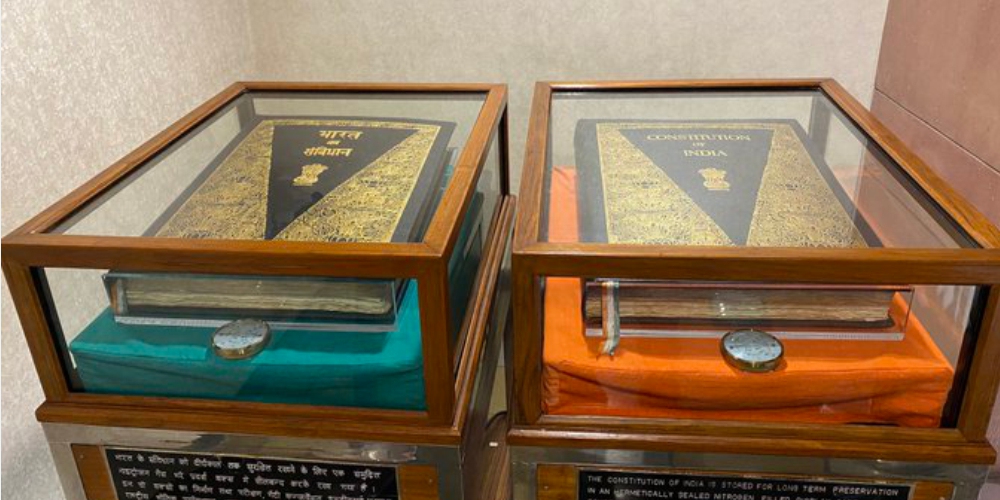

The Indian Parliament’s Library employs unique helium-filled cases designed to safeguard the original copies of the Indian Constitution. This innovative approach aims to prevent the oxidation of ink, ensuring the long-term preservation of this historic document.
4. The Time It Took in the Making:
The Constituent Assembly convened on December 9, 1946, and the final version of the constitution was adopted on November 26, 1949. The total time it took for the constitution to be drafted was 2 years, 11 months, and 18 days. It came into effect on January 26, 1950, marking the official establishment of the Republic of India.
5. Illustration of the Constitution:
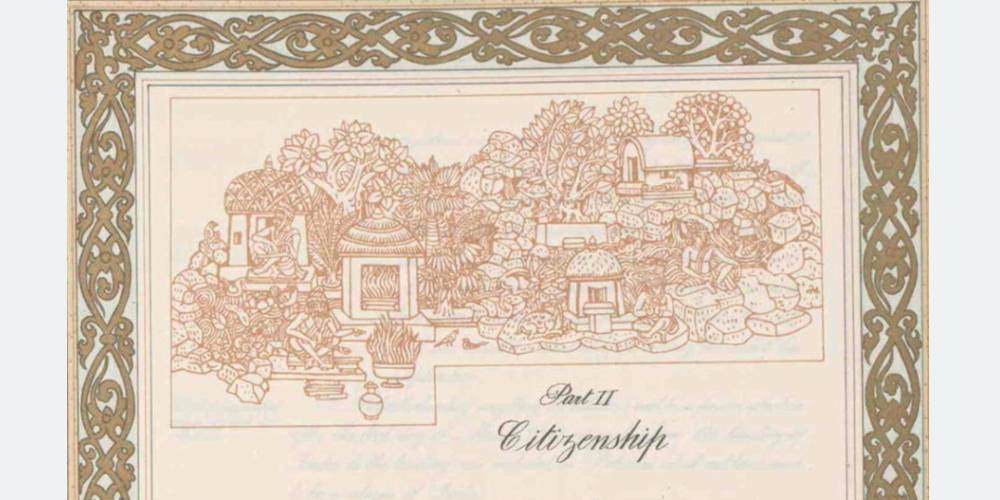
The pages of the handwritten Indian Constitution, including the Preamble, bear artistic illustrations by Shantiniketan painters such as Beohar Rammanohar Sinha and Nandalal Bose. This creative touch adds a unique aesthetic dimension to the constitutional document.
6. Number of Amendments in the first draft
This fact about Indian Constitution reflects the scale of thought, discussion & evaluation that went into the making of the Constitution. The initial draft of the Indian Constitution underwent over 2000 amendments. This extensive process not only replaced the Government of India Act, 1935, but also marked the transition from the Dominion of India to the establishment of the Republic of India.
7. Various Borrowed Elements from Other Constitutions
The Indian Constitution incorporates elements from various global constitutional models that align with the unique challenges and aspirations of the country. The Constituent Assembly carefully selected and adapted features from diverse sources to create a distinct constitutional framework.
Among the features derived from the Government of India Act, 1935, are:
- Federal Scheme
- Office of Governor
- Judiciary
- Public Service Commissions
- Emergency Provisions
- Administrative Details
Provisions that were adapted from different international constitutions are provided in detail the table below:
| S.No | Countries | Borrowed Features of Indian Constitution |
| 1 | Australia | Concurrent list |
| Freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse | ||
| Joint-sitting of the two Houses of Parliament | ||
| 2 | Canada | Federation with a strong Centre |
| Vesting of residuary powers in the Centre | ||
| Appointment of state governors by the Centre | ||
| Advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court | ||
| 3 | France | Republic |
| Ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity in the Preamble | ||
| 4 | Germany (Weimar) | Suspension of Fundamental Rights during emergency |
| 5 | Ireland | Directive Principles of State Policy |
| Nomination of members to Rajya Sabha | ||
| Method of election of the president | ||
| 6 | Japan | Procedure Established by law |
| 7 | Soviet Union (USSR) (now, Russia) | Fundamental duties |
| Ideals of justice (social, economic and political) in the Preamble | ||
| 8 | South Africa | Procedure for amendment in the Indian Constitution |
| Election of members of Rajya Sabha | ||
| 9 | UK | Parliamentary government |
| Rule of Law | ||
| Legislative procedure | ||
| Single Citizenship | ||
| Cabinet system | ||
| Prerogative writs | ||
| Parliamentary privileges | ||
| Bicameralism | ||
| 10 | US | Fundamental rights |
| Independence of judiciary | ||
| Judicial review | ||
| Impeachment of the president | ||
| Removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges | ||
| Post of vice-president |
Conclusion
As we celebrate Republic Day 2024, it’s essential to reflect on the remarkable facets of the Indian Constitution that have shaped the nation’s destiny. The interesting facts about Indian Constitution highlighted in this blog underscore the foresight, inclusivity, and resilience embedded in the Constitution of India by the founding fathers of the country. From being the longest-written constitution in the world to championing fundamental rights and ensuring social justice, the Indian Constitution stands as a testament to the visionary leaders who drafted it.


Thank you so much very valuable words and good information thanks 🙏🙏🙏
HAPPY RIPUBLIC DAY 2024🇮🇳🇮🇳🇮🇳
Super